Within the entire cutting system, the proper use of the cutting tool significantly impacts the final cutting results. To fully leverage the characteristics of PCBN tool material, besides rationally selecting high-speed, high-rigidity machine tools and choosing appropriate tool material grades and cutting edge parameters, reasonable cutting parameters should also be selected based on specific machining conditions to better "match" the workpiece material being machined.

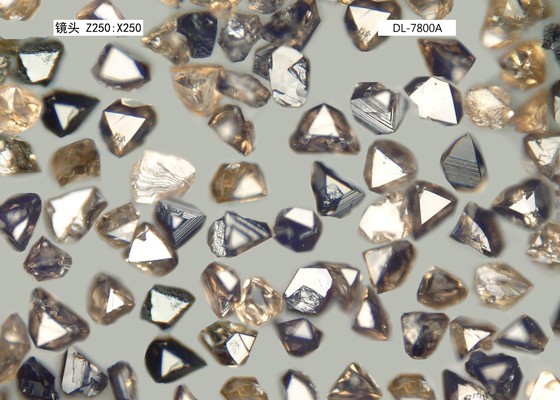
The grain size of PCBN material is broadly categorized into three types: coarse grain (20~50 μm), medium grain (10~20 μm), and fine grain (1~10 μm). Larger grain size provides better wear resistance and longer tool life, but results in poorer cutting edge quality and difficulty in achieving good surface roughness. Conversely, fine grain tools offer better cutting edge quality and improved machined surface quality, but have poorer wear resistance. The specific choice depends on the requirements of different processes (like roughing or finishing) to select tool material grades with different grain sizes.
The performance of PCBN is related to the CBN grain size, CBN content, and the type of binder. Generally, based on CBN content, it can be divided into two categories: one is high CBN content (above 70%), suitable for cutting heat-resistant alloys, cast iron, and ferrous sintered metals, such as Berlt grades BT2800, BT3500, BT7800; the other is low CBN content (50%~70%), suitable for cutting hardened steel, such as Berlt grades BT6000, BT6500.
Simultaneously, due to the relatively high brittleness of cubic boron nitride material, to enhance the strength of the cutting edge, a negative chamfer must be ground on the cutting edge, and the tool nose should be appropriately rounded. However, increasing the nose radius and negative chamfer will increase cutting forces and the chance of chatter. Therefore, when the rigidity of the machine tool-fixture-tool-workpiece system is insufficient, excessively large nose radii and negative chamfers should not be used.
Cubic boron nitride tools are generally used for dry cutting, but wet cutting is also employed for some workpiece materials. Although PCBN tools can withstand cutting temperatures of 1250~1350°C, it's important to note that CBN undergoes hydrolysis with water vapor at high temperatures (around 1000°C), accelerating tool wear. Consequently, during wet cutting, water-based solutions should never be used as cutting fluid.