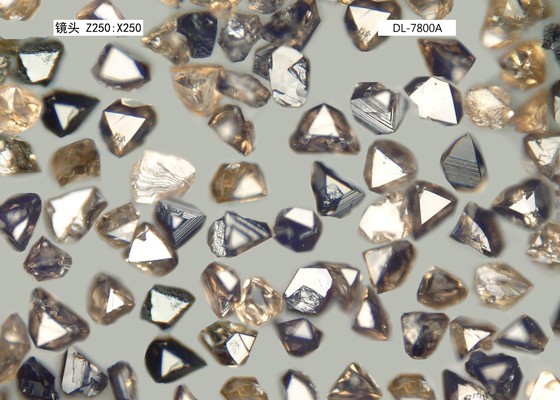
In the machining of high-hardness materials, PCBN (Polycrystalline Cubic Boron Nitride) inserts are highly favored due to their exceptional hardness and thermal stability. However, even ultra-hard materials are inevitably subject to wear. This article by Zhengzhou Bote will discuss the main causes of PCBN insert wear during actual cutting processes.

1、Diffusion/Chemical Wear
Under high-speed or heavy-load cutting conditions, the temperature on the tool’s rake and flank faces can rise to several hundred degrees or even higher. In such high-temperature environments, atomic diffusion, oxidation, and chemical reactions may occur between the tool and the chips or workpiece material.
Impact on Tool Life: Diffusion/chemical wear is typically a slow and continuous erosion process. However, once a critical point is reached, the tool’s performance declines sharply, leading to deteriorated surface quality and accelerated wear.
Solutions: Use binders and processes with better high-temperature resistance and oxidation resistance; optimize cutting parameters; enhance the tool’s thermal conductivity.
2、Grain Spalling and Micro-Chipping
PCBN inserts are composed of numerous tiny CBN grains and binders, with micro-cracks and impurities often present between grains and at grain boundaries. During the cutting process, due to contact between the chips and the cutting edge or impact loads, some CBN grains may detach from the grain boundaries, resulting in micro-spalling or micro-chipping.
Impact on Tool Life: Micro-chipping and spalling usually start from the cutting edge. Once they begin to spread, the cutting edge geometry changes, leading to an imbalance in cutting force distribution and accelerated wear. When the chipping becomes severe, the tool reaches a state of failure.
Solutions: Select high-quality CBN insert materials with tighter grain boundary structures and lower impurity content; treat the cutting edge to enhance its geometric stability; maintain high rigidity and low vibration in the tool system.
3、Crater Wear and Groove Wear
These two types of wear are relatively common in PCBN tools. Crater wear occurs on the rake face due to continuous friction, diffusion, and adhesive wear, forming a crescent-shaped depression near the tool tip. Groove wear occurs on the flank face due to uneven chip flow velocity and intense friction, creating grooves or channels at specific localized positions along the flank face.
Impact on Tool Life: Crater wear alters the geometric characteristics of the rake face, affecting cutting force distribution, chip flow, and machining accuracy. Groove wear may cause interference on the flank face and increase dimensional errors.
Solutions: Choose appropriate cutting speeds and feed rates to avoid excessive wear caused by overly high speeds; optimize the geometric structure of the cutting edge; ensure workpiece stability, reduce vibrations, and improve overall system rigidity.
Although PCBN inserts possess excellent wear resistance and thermal stability, their lifespan in complex cutting environments heavily depends on the control of wear mechanisms. By deeply understanding mechanisms such as diffusion/chemical wear, grain spalling and micro-chipping, as well as crater/groove wear, more targeted efforts can be made in terms of materials, parameters, cooling, and system rigidity.