In the modern mechanical manufacturing industry, CBN (cubic boron nitride) inserts and ceramic inserts are two very typical types of cutting tool materials. With performance surpassing traditional cemented carbides, they have become essential tools for machining difficult-to-cut materials such as high-temperature alloys and hardened steel.
However, although both belong to common cutting tools in machining, they exhibit significant differences in performance and application. Selecting the appropriate insert material based on the workpiece material is crucial to unlocking the tool's maximum value.
I. Intrinsic Material Properties
CBN Inserts: Cubic Boron Nitride (CBN) is a synthetic superhard material, second only to diamond in hardness. Polycrystalline cubic boron nitride (PCBN) inserts are formed by sintering CBN micropowder particles with a binder under high temperature and high pressure. Their core advantages lie in extremely high hardness, excellent thermal stability, and chemical inertness. They are particularly adept at machining ferrous metals.
Ceramic Inserts: Typically based on high-purity alumina (Al₂O₃) or silicon nitride (Si₃N₄), they are sintered using powder metallurgy processes. Modern ceramic inserts are mostly toughened composite ceramics. Their advantages include extremely high heat resistance, wear resistance, and chemical stability, but their hardness and toughness are lower than CBN.
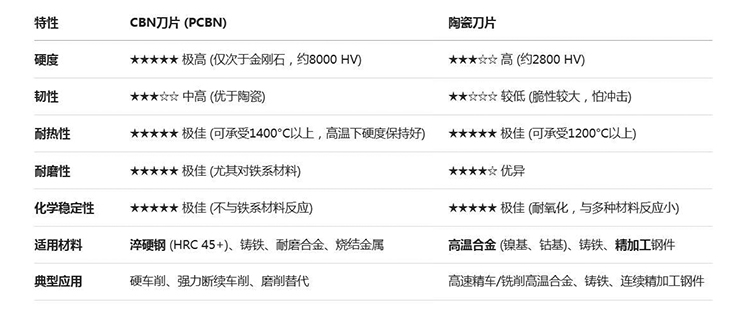
II. Performance and Application Scenario Comparison
III. Rational Selection and Usage
Select CBN Inserts: Prioritize CBN inserts when facing materials with hardness exceeding HRC 45, such as hardened steel or chilled cast iron; choose CBN inserts with better toughness when the machining conditions involve some impact or vibration; in hard turning, replace grinding operations ("replacing grinding with turning") to improve machining efficiency.
Select Ceramic Inserts: For continuous or light-interrupted machining of nickel-based, cobalt-based, and other high-temperature alloys, ceramic inserts offer superior advantages in heat resistance and chemical stability; under stable conditions for finishing, ceramics can provide superior surface quality to a certain extent.